🧪 What Are Tea Polyphenols?
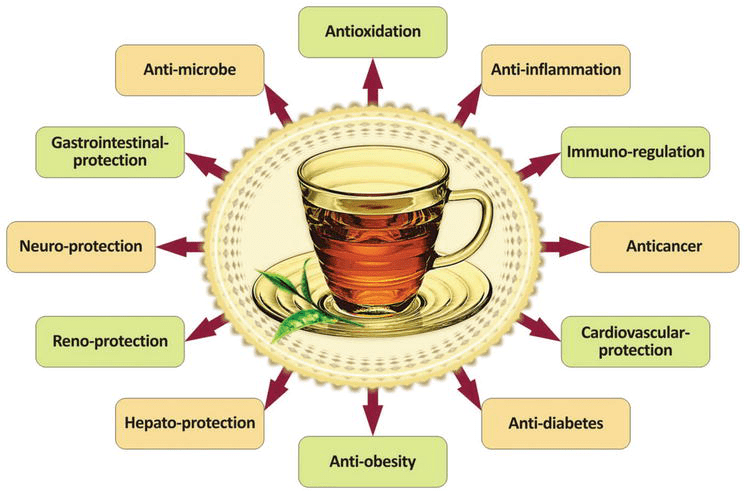
Tea polyphenols are natural compounds found abundantly in tea leaves, especially in green, oolong, and black tea. They belong to a class of antioxidants called flavonoids, and include key compounds like epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), catechins, and theaflavins.
These compounds are not just for flavor—they offer a wide range of scientifically studied health benefits.
🔬 Scientifically Backed Health Benefits of Tea Polyphenols
✅ 1. Powerful Antioxidant Activity
Tea polyphenols can neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, which plays a key role in aging and many chronic diseases.
Evidence:
A 2010 review in Molecular Nutrition & Food Research confirmed that EGCG and other catechins help protect DNA, lipids, and proteins from oxidative damage.
🫀 2. Cardiovascular Health
Regular consumption of tea polyphenols is associated with lower blood pressure, improved cholesterol profiles, and reduced risk of heart disease.
Evidence:
A large meta-analysis (American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2011) showed that green tea consumption significantly reduced LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
💪 3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Tea polyphenols help reduce chronic low-grade inflammation, which is linked to diseases like diabetes, cancer, and Alzheimer’s.
Mechanism:
They downregulate inflammatory pathways such as NF-κB and cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6.
🧠 4. Neuroprotection & Brain Health
EGCG and related compounds have been shown to protect neurons, improve memory, and may help prevent neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
Evidence:
A 2017 study published in Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience noted EGCG’s ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and reduce neuroinflammation.
⚖️ 5. Weight Management & Metabolism
Tea polyphenols may boost metabolism, enhance fat oxidation, and help regulate blood sugar levels, making them useful in weight control and metabolic health.
Evidence:
Several clinical trials, including one in Obesity Reviews (2009), found green tea catechins increased fat burning during exercise and rest.
🦠 6. Antimicrobial & Gut Health Benefits
Tea polyphenols exhibit antibacterial, antiviral, and prebiotic-like effects. They can support gut microbiota balance and inhibit harmful pathogens.
Evidence:
EGCG inhibits the growth of Helicobacter pylori (linked to ulcers) and promotes beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium, per a 2015 study in Food & Function.
🍵 Not All Tea Is Equal
The type of tea and processing method significantly affect the polyphenol content:
| Tea Type | Key Polyphenols | Typical Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Green Tea | EGCG, catechins | High antioxidant, fresh |
| Oolong Tea | Catechins + theaflavins | Balanced, smooth |
| Black Tea | Theaflavins, thearubigins | Strong, full-bodied |
Kombucha fermented on different tea bases (e.g., green vs black) can therefore provide distinct functional profiles.
⚠️ Tips & Considerations
- Dosage matters: 2–3 cups of tea per day or equivalent extract is considered effective.
- Excessive intake may interfere with iron absorption—moderation is key.
- Best absorbed on an empty stomach or between meals.
🥂 Final Sip
So next time you sip your kombucha, remember —
you’re not just drinking a trendy probiotic…
you’re sipping centuries of tea wisdom + modern fermentation magic.
All thanks to our leafy friends: tea polyphenols. 🌿
Leave a comment